(1) Failure phenomenon: the pump can not discharge material ;Failure causes
Failure causes: a. Rotating in the opposite direction; b. Suction or discharge valve is closed; c. Inlet no material or pressure is too low; d. Viscosity is too high, the pump can not bite the material
Countermeasures: a. Confirmation of the direction of rotation; b. Confirmation of whether the valve is closed; c. Check the valve and pressure gauge; d. Check the viscosity of the liquid to run at low speeds proportional to the speed of the flow rate is not appearing, if there is a flow rate, then the inflow is insufficient.
(2) Failure phenomenon: insufficient pump flow
Failure causes: a. Suction or discharge valve closed; b. Inlet pressure is low; c. Export pipeline blockage; d. Stuffing box leakage; e. Low speed
Countermeasures: a. Confirm whether the valve is closed; b. Check whether the valve is open; c. Confirm whether the discharge volume is normal; d. Tighten; when a large number of leakage leakage affects the production, it should be stopped and disassembled for inspection; e. Check the actual speed of the pump shaft;

(3) Fault phenomenon: abnormal sound
Failure causes: a. Coupling eccentricity or poor lubrication b. Motor failure; c. Reducer abnormal; d. Poorly installed at the shaft seal; e. Shaft deformation or wear
Countermeasures: a. Find the right or fill the grease; b. Check the motor; c. Check the bearings and gears; d. Check the shaft seal; e. Stop the car to dismantle the body for inspection
(4) Fault phenomenon: excessive current
Fault causes: a. Excessive outlet pressure; b. Excessive melt viscosity; c. Poorly assembled shaft seals; d. Worn shafts or bearings; e. Motor failure
Countermeasures: a. Check the downstream equipment and pipeline; b. Check the viscosity; c. Check the shaft seal and adjust it appropriately; d. Check after stopping the machine, and check if it is too heavy by hand coiling; e. Check the motor
(5) Failure phenomenon: pump suddenly stop
Failure causes: a. Power failure; b. Motor overload protection; c. Damaged coupling; d. Exit pressure is too high, the interlock reaction; e. Pump bite into the abnormal; f. Shaft and bearing adhesion jamming
Countermeasures: a. Check the power supply; b. Check the motor; c. Open the safety cover and check the disk; d. Check the instrument interlocking system; e. After stopping, forward and reverse rotation to confirm; f. Coil confirmation
Note: The above fault phenomena and countermeasures are one-to-one correspondence.
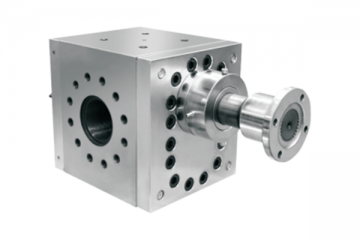
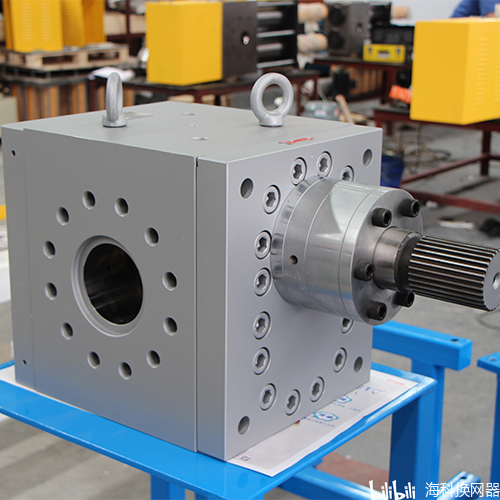
Heiko specializes in the manufacture of all types of melt pumps and screen changers.